Your Questions About Natural Gas, Answered
Natural gas is powering our modern way of life and helping to cut CO2 emissions. Here’s what this energy revolution is all about.
Learn MoreNatural gas is powering our modern way of life and helping to cut CO2 emissions. Here’s what this energy revolution is all about.
Learn MoreHow American energy exports are driving down carbon emissions worldwide

September 25, 2020
Natural gas has made for a more reliable and affordable source of energy to fuel American homes, businesses, and industries, while also helping to reduce the nation’s greenhouse gas emissions by shifting away from coal as the nation’s main power source. In fact, coal generation in the U.S. dropped from 50% to 24% between 2005 and 2019, while natural gas generation increased from 19% to nearly 40% in that time, with natural gas overtaking coal as the predominant source of electricity generation since 2016.
Now, other countries are joining the cleaner energy movement— and access to American liquefied natural gas is helping to make that possible.
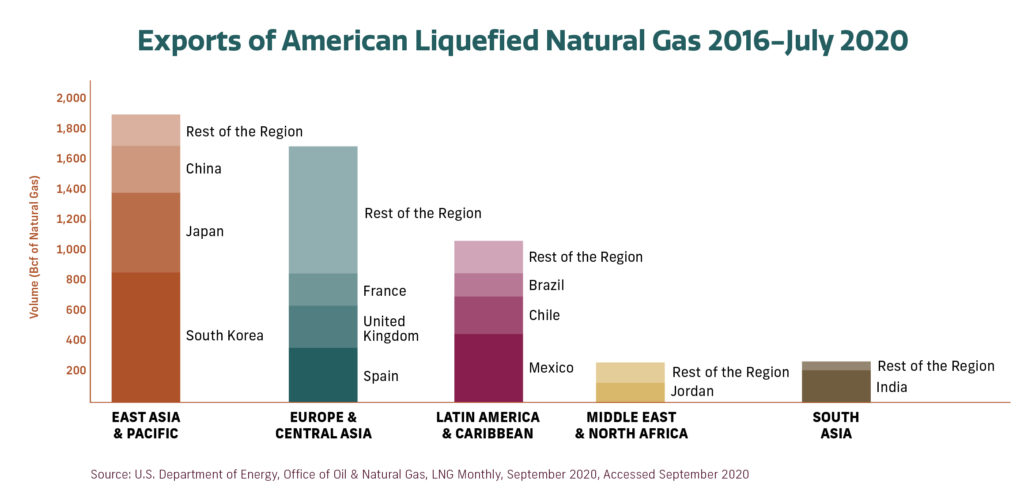
Liquefied natural gas, or LNG, is natural gas cooled to a liquid state, making it possible to ship to regions or countries that demand gas for power generation, petrochemicals, and other application. Today, LNG is the fastest-growing gas supply source, and demand for it is expected to increase worldwide as more nations turn to affordable and cleaner energy solutions.
Improving Air in China
China — the most populous nation in the world with nearly 1.4 billion residents — is working to build out its natural gas capacity. In the last few years, China has become one of the world’s largest natural gas importers.
Efforts to reduce air pollution, including emissions of nitrous oxides, sulphuric oxides and particulate matter, and the health challenges it poses to people living there, is also a major driver behind this shift. China ranks among the top 10 countries with the most deaths caused by air pollution, due to toxic smog lingering over its cities from using coal. According to a 2019 LNG report from Shell, switching from coal to gas has contributed to a 78% improvement in Beijing’s winter air quality over the last five years.
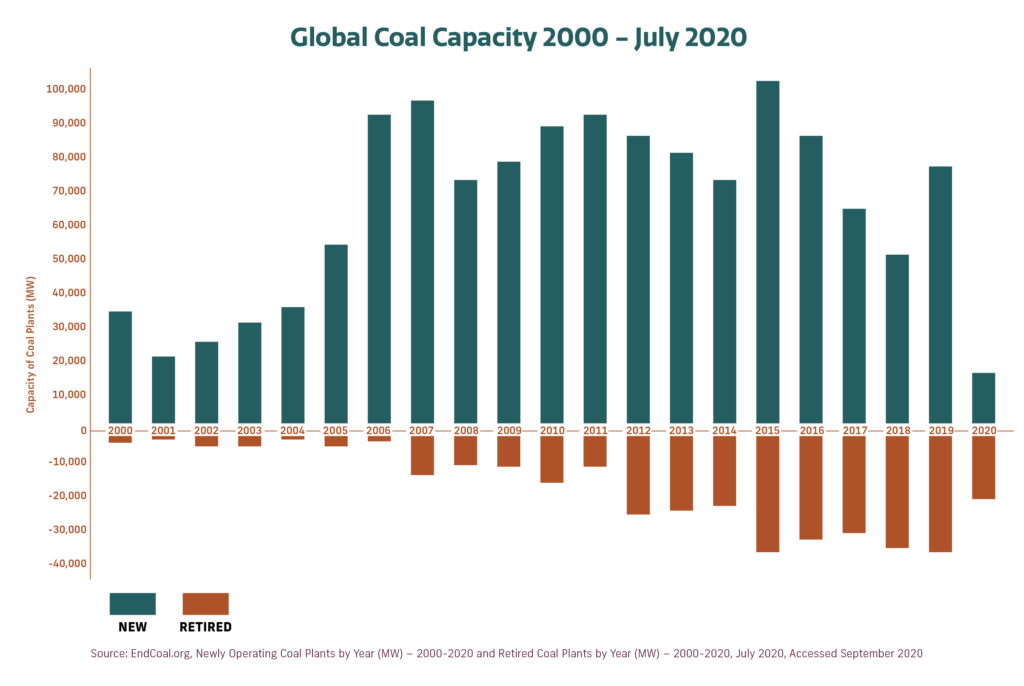
Driving Down Carbon Emissions
According to a recent API study, American natural gas will play a critical role in reducing carbon dioxide emissions worldwide. In fact, using U.S. LNG instead of coal for electricity generation in China, Germany, and India produces, on average, 50.5% fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
Balancing energy needs at home with environmental concerns has long been a priority in the U.S. Over the last decade, the country has reduced carbon dioxide emissions in the power sector by 28%, and natural gas has played a major role in achieving that goal. This success at home will likely serve as a model for other countries looking to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and still provide a stable source of energy to their people.
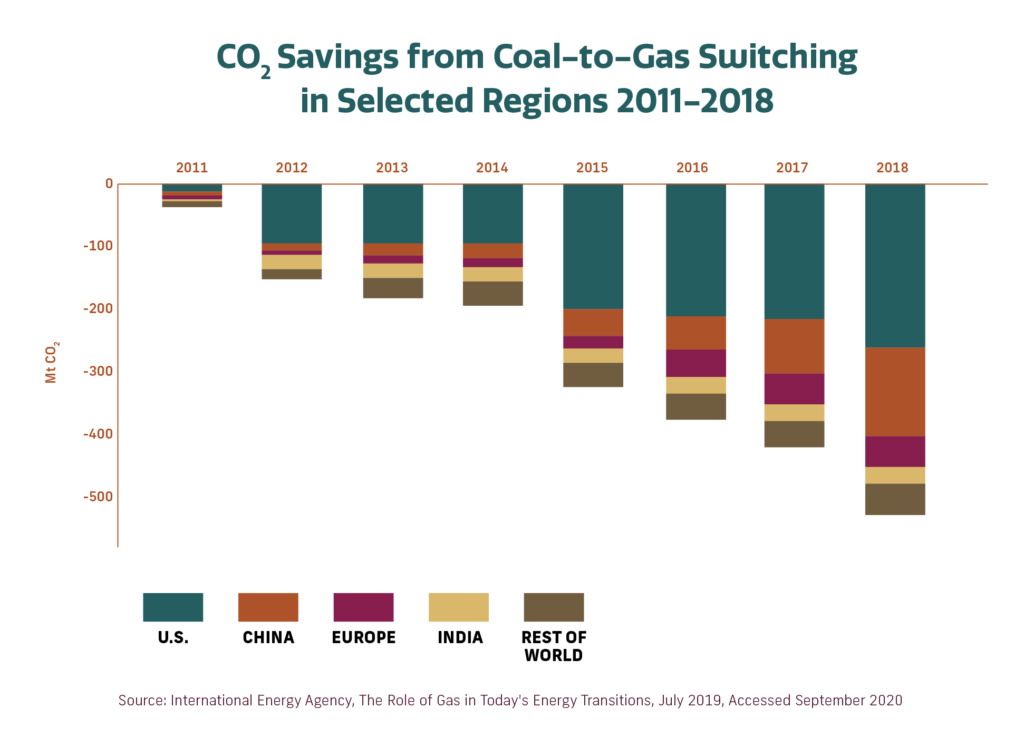
“U.S. LNG exports can help accelerate environmental progress across the globe, enabling nations to transition to cleaner natural gas to reduce emissions and address the global risks of climate change,” said Dustin Meyer, API Director of Market Development.
What is the single biggest reason for the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions in the United States?
Correct! The U.S. Energy Information Administration reported that from 2005-2019, 65% of the decline in CO2 emissions in the electric power sector was attributable to switching from coal-fired to natural gas-fired electricity generation. Learn more about the power of natural gas.
Good try! The U.S. Energy Information Administration reported that from 2005-2019, 65% of the decline in CO2 emissions in the electric power sector was attributable to the switching from coal-fired to natural gas-fired electricity generation. Learn more.
More From API
Read on for in-depth articles about how we’re securing America’s energy future, our efforts to combat climate change, and more.
New innovations make it possible to produce more energy with fewer emissions Combatting emissions of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, […]
Learn MoreBetween now and 2050, according to the Energy Information Administration, the American demand for electricity will increase 1% each year. To […]
Learn MoreWe’re taking five key steps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Learn MoreWe use cookies to offer you a better browsing experience, analyze site traffic, personalize content, and serve targeted advertisements. If you continue to use this site, you consent to the use of cookies. Read more about our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions.
accept